|
# An example of using the sliders module.
# Malcolm Kesseon
# 28 July 2020
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
from sliders import *
class Demo_Sliders(QDialog):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
QDialog.__init__(self, parent)
# Ensure our window stays in front and give it a title
self.setWindowFlags(Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint)
self.setWindowTitle("DemoDialog")
self.setFixedSize(400, 200)
# Create and assign the main (vertical) layout.
vlayout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(vlayout)
self.addSlidersPanel(vlayout)
self.addButtonPanel(vlayout)
self.show()
#--------------------------------------------------------------------
def addSlidersPanel(self, parentLayout):
vlayout = QVBoxLayout()
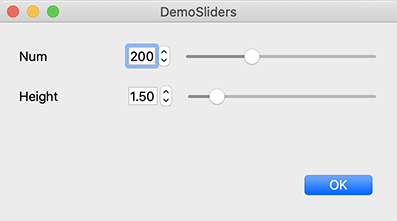
self.num = IntSlider("Num", 100, 400, 200, vlayout)
self.height = FloatSlider("Height", 1.0, 5.0, 1.5, vlayout)
parentLayout.addLayout(vlayout)
#--------------------------------------------------------------------
def addButtonPanel(self, parentLayout):
# Add a Button and connect it to our custom buttonAction() method.
self.button = QPushButton("OK")
self.button.clicked.connect(self.buttonAction)
# For easthetics we add the button to a horizonal layout and use
# stretch() to ensure it is pushed to the right hand edge.
hlayout = QHBoxLayout()
hlayout.addStretch()
hlayout.addWidget(self.button)
parentLayout.addLayout(hlayout)
#--------------------------------------------------------------------
# Confirm the slider values can be read
def buttonAction(self):
print(str(self.height.getValue()))
print(str(self.num.getValue()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create the Qt Application
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
demo = Demo_Sliders()
demo.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
|