Introduction
This tutorial provides an explanation of how spheres can be rendered at the vertices of a
polymesh by the use of a procedural primitive written in C/C++. The reader should review
the tutorials,
C++ Development Environment
Procedural Primitives: Getting Started
Procedural Primitives: Adding an Interface

Figure 1 (rollover)
The Procedural Primitive Code
Open the PlaceSpheresProc.cpp file and build the DSO using the keyboard shortcut Alt + e or Control + e.
A DSO (dynamic shared object) called PlaceSpheresProc.dll (Windows) or PlaceSpheresProc.so (OSX and Linux)
will be created either in the same folder as the PlaceSpheresProc.cpp, or, if Cutter's preferences have been
set as described in
C++ Development Environment the DSO will can
be found in,
maya/rfm_scripts/proc_prims
The Python Code
Copy or move the pp_place_spheres.py script to either your
maya/script folder, or your
maya/rfm_scripts folder.
Using the Scripts in Maya
Either use the Maya scene provided in the PlaceSpheres.zip or follow these instructions.
Assuming a project directory called "PlaceSpheres" has been set in Maya, create a simple polymesh
object such as a torus.
From the RenderMan menu choose Archive->Create Procedural Node.
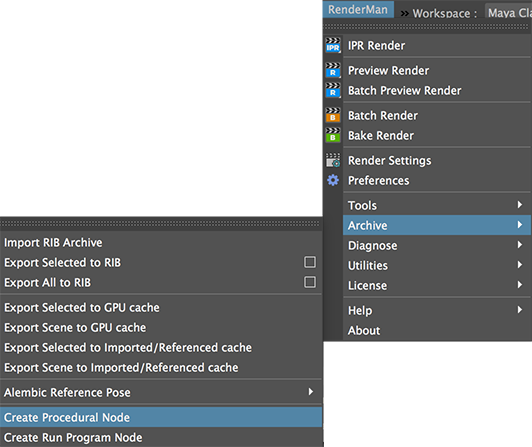
Figure 2
In Maya's outliner choose, Display->Shapes.
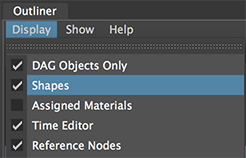
Figure 3
Parent the RenderManProgram node to the torus.
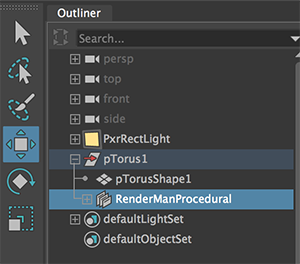
Figure 4
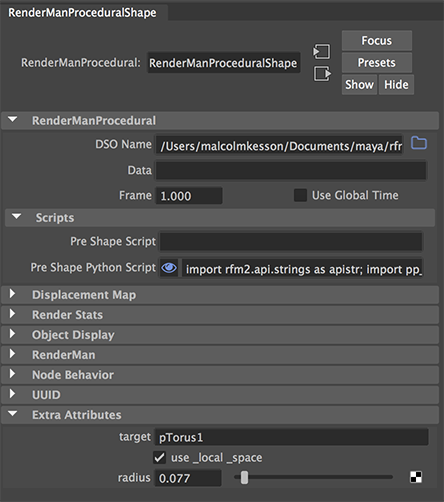
In the outliner select the RenderManProgramShape shape node.
In the Attribute Editor for the RenderManProgramShape choose,
Attributes->Add Attributes...
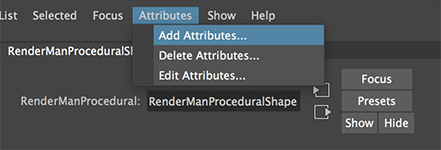
Figure 5