Rib
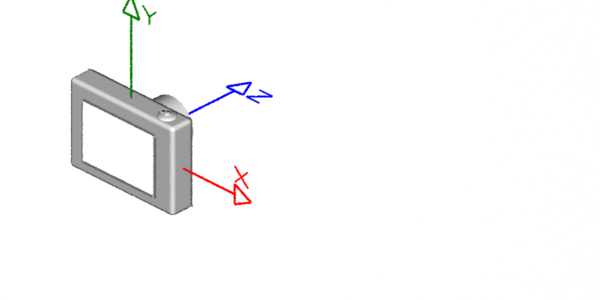
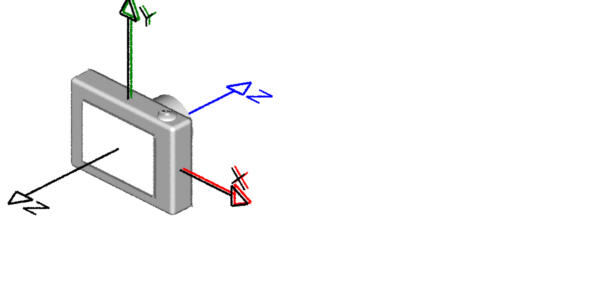
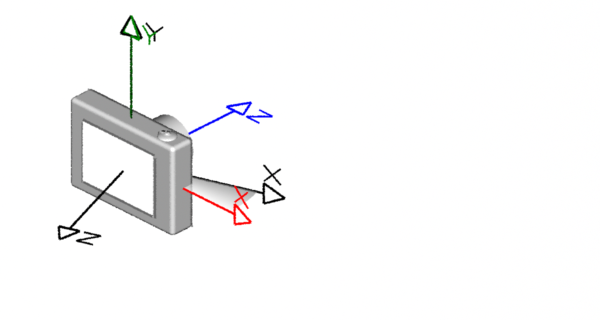
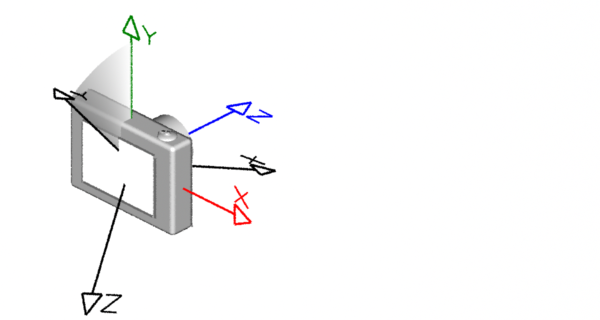
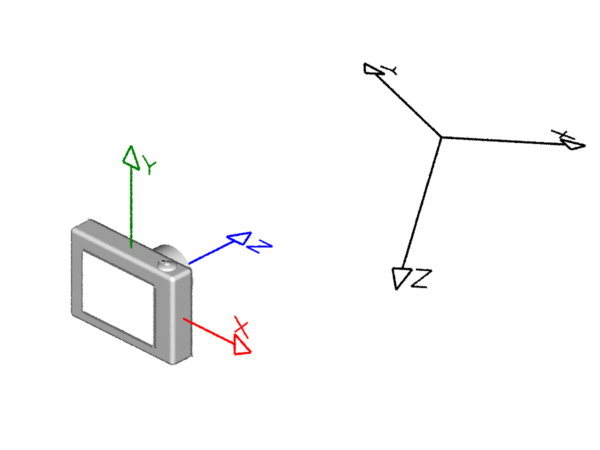
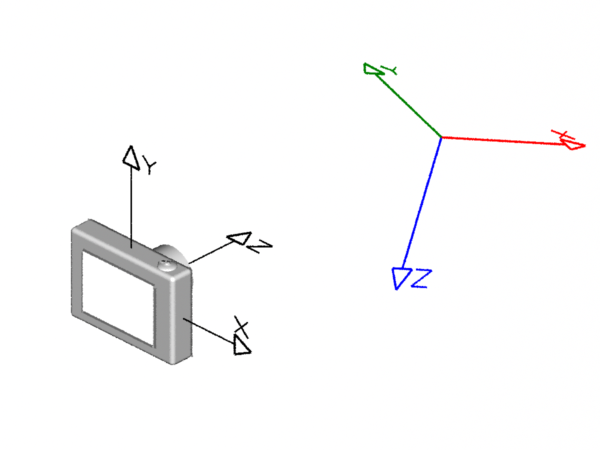
Left-hand & Right-hand Coordinate Systems
# disk_poly.rib
# left hand renderman coordinate system
# right hand world coordinate system
Display "disk_poly" "framebuffer" "rgb"
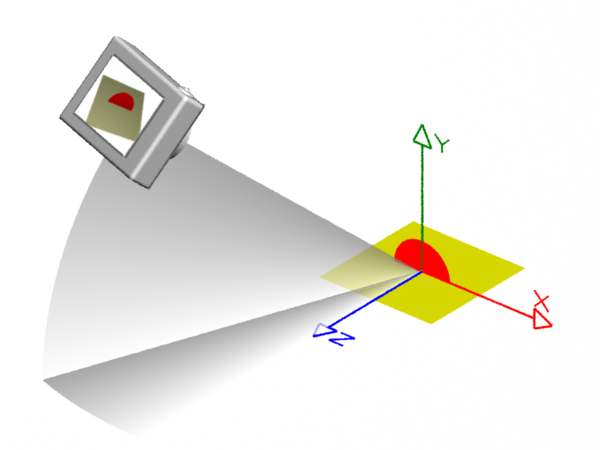
Projection "perspective" "fov" 40
Format 320 240 1
Translate 0 0 3
Rotate -40 1 0 0
Rotate -20 0 1 0
Scale 1 1 -1 # <-- Note the negative z scale
WorldBegin
Color 1 1 0.7
Polygon "P" [-0.5 0 -0.5 -0.5 0 0.5 0.5 0 0.5 0.5 0 -0.5]
"st" [0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0]
Color 1 0 0
Disk 0 0.25 360
WorldEnd
|
Coordinate systems come in two flavors, left-hand ("lh") and right-hand ("rh"). As shown below, the handedness of a coodinate system determines whether a positive rotation is clockwise or anti-clockwise. The thumb and fingers of either the left or right hand can be used to visualize the direction a positive rotation. For example, to decide whether a positive rotation around the x-axis of a right-hand coordinate system is clockwise or anti-clockwise point the thumb of the right hand along the x-axis; the "curl" of your fingers will indicate the direction of the rotation is clock-wise.
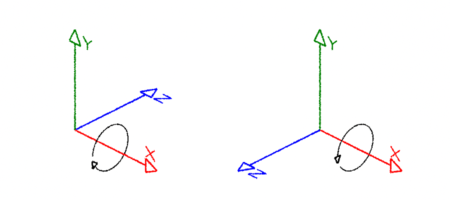
Left-hand (RenderMan) Right-hand (Maya & Houdini)
Rib Files Written by Pixar's RMS & RAT
Unlike RenderMan, most 3D modeling applications use right-hand coordinates.
Rib files generated by Maya, and Pixar's RenderMan Studio (RMS), apply a negative z scaling
to the viewing transformations. The scaling ensures the coordinate system of the
WorldBegin / WorldEnd block is right-handed. The predecessor to RMS,
a product from Pixar known as RenderMan Artist Tools (RAT) also inserted a ReverseOrientation
statement immediately after WorldBegin. This was necessary because RAT, despite the
use of a right-hand world block, specified surface data (vertices of polygons etc) in left-hand
order. The ReverseOrientation ensured that surface normals were correctly orientated.
The Maya plugin for RMS, RenderMan for Maya Pro (RfM Pro) writes surface data in right-hand order
and as such the call to ReverseOrientation is not required.
Rib Files Written by Side Effects Houdini
The "handedness" of surfaces written by Side Effects Houdini is similiar to RAT. However, instead
of using ReverseOrientation their rib files use,
Orientation "rh"
immediately after WorldBegin to ensure that surface normals are correctly orientated.
Rib Files Written by Cutter
Rib files generated by Cutter as well as those listed in the Fundza tutorials conform to RMS in the sense that the world block is right-handed and vertices are listed in right-hand order.
Rib Files and Pixar's Technical Documentation
Traditionally, example rib files listed in Pixar's documentation specify a left-hand camera and a left-hand world block. In other words the negative z axis of the world is "pointing" at the camera. Whereas the rib files from RMS, RAT, Houdini and Cutter specify a right-hand world block in which the positive axis of the world is "pointing" at the camera.
Issues with Surface Normals and Quadrics
While ReverseOrientation corrects the reversed normals in rib files written
by RAT (actually, its Maya plugin called "mtor") it has an undesired side-effect on quardics
and as such unfortunately causes them to become reversed!
This is not an issue for Maya and Houndini because their tool kit of surfaces do not
include quadrics. However, the unexpected flipping of the surface normals of quadrics
is very significant when dealing with hand-written rib files that include the use of the
ReverseOrientation statement. More information can be found about this issue
in the tutorial
"RenderMan: Reverse Orientation & Quadrics".